Diabetic neuropathy is a common complication of diabetes that can significantly affect quality of life. This article delves into what diabetic neuropathy is, how it develops, its symptoms, and the various treatment options available to help manage this condition effectively.
What is Diabetic Neuropathy?
Diabetic neuropathy refers to a group of nerve disorders that occur as a result of diabetes. High blood sugar levels can damage nerves throughout the body, leading to a range of symptoms, particularly in the legs and feet. It is one of the most common long-term complications of diabetes, affecting up to 50% of individuals with diabetes over time.
Causes of Diabetic Neuropathy
The exact cause of diabetic neuropathy is not fully understood, but several factors contribute to its development, including:
- High Blood Sugar Levels: Chronic hyperglycemia can lead to nerve damage. Over time, excess glucose in the blood can cause biochemical changes that harm nerve fibers.
- Duration of Diabetes: The longer a person has diabetes, the greater the risk of developing neuropathy. Individuals with poorly controlled diabetes are at higher risk.
- Genetic Factors: Some people may have a genetic predisposition to nerve damage, making them more susceptible to diabetic neuropathy.
- Other Health Conditions: Conditions such as high blood pressure, obesity, and high cholesterol can contribute to nerve damage in diabetic patients.
- Alcohol Use and Tobacco: Excessive alcohol consumption and smoking can further damage nerves and exacerbate symptoms.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of certain nutrients, particularly vitamin B12, can lead to nerve damage, particularly in those with diabetes.
Symptoms of Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy can manifest in various forms, and symptoms can differ depending on the type of neuropathy. Common types include peripheral neuropathy, autonomic neuropathy, and focal neuropathy.
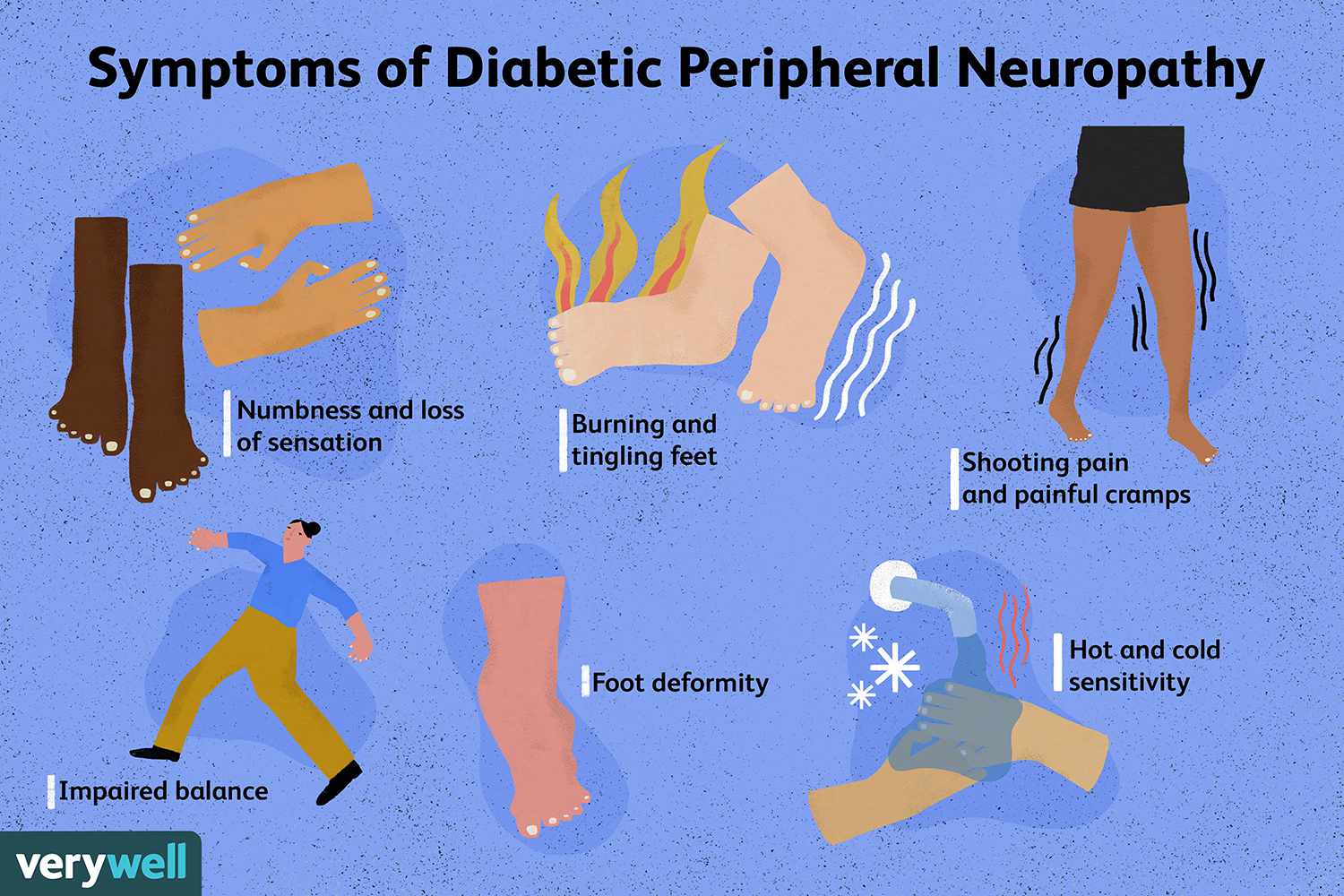
1. Peripheral Neuropathy
This is the most common form, affecting the extremities. Symptoms may include:
- Numbness or tingling in the feet and hands
- Burning sensations or sharp, stabbing pain
- Increased sensitivity to touch
- Weakness in the limbs
- Difficulty walking or maintaining balance
2. Autonomic Neuropathy
This affects the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily functions. Symptoms can include:
- Digestive issues (nausea, bloating, diarrhea, or constipation)
- Abnormal blood pressure and heart rate
- Sexual dysfunction
- Inability to sense hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)
3. Focal Neuropathy
This type affects specific nerves and can lead to sudden weakness or pain in a particular area. Symptoms may include:
- Vision problems (e.g., double vision)
- Pain in the lower back, pelvis, or abdomen
- Nerve palsies affecting the eye or facial muscles
Treatment Options for Diabetic Neuropathy
While there is no cure for diabetic neuropathy, several treatment options can help relieve symptoms and manage the condition effectively.
1. Blood Sugar Management
The primary focus in treating diabetic neuropathy is maintaining optimal blood sugar levels. Tight control of blood glucose can slow the progression of nerve damage and alleviate symptoms. This may involve:
- Medications (e.g., insulin or oral hypoglycemics)
- Regular blood sugar monitoring
- Adopting a diabetes-friendly diet
- Engaging in regular physical activity
2. Pain Relief Medications
Various medications can help manage nerve pain associated with diabetic neuropathy, including:
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen may provide mild relief.
- Prescription Medications: Antidepressants (such as duloxetine) and anticonvulsants (like gabapentin) can be effective in managing nerve pain.
- Topical Treatments: Capsaicin cream or lidocaine patches can provide localized pain relief.
3. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can improve strength, coordination, and mobility. A physical therapist can recommend exercises tailored to individual needs, helping to enhance balance and prevent falls.
4. Lifestyle Modifications
Certain lifestyle changes can improve symptoms and overall health:
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support nerve health.
- Exercise: Regular low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling can improve circulation and nerve function.
- Avoiding Alcohol and Tobacco: Reducing or eliminating these substances can help manage symptoms and improve overall health.
5. Complementary Therapies
Some individuals may find relief through complementary therapies such as:
- Acupuncture: This ancient practice may help alleviate pain for some people.
- Massage Therapy: Gentle massage can improve circulation and reduce pain.
- Mind-Body Techniques: Practices like yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can help manage pain and stress.
Conclusion
Diabetic neuropathy is a serious complication of diabetes that can significantly impact quality of life. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management. By prioritizing blood sugar control and incorporating lifestyle changes, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing neuropathy and manage symptoms if they arise. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.

