Peptic ulcers are a prevalent health issue that can cause significant discomfort and complications if left untreated. This comprehensive guide will help you understand what peptic ulcers are, their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and tips for prevention.
What Are Peptic Ulcers?
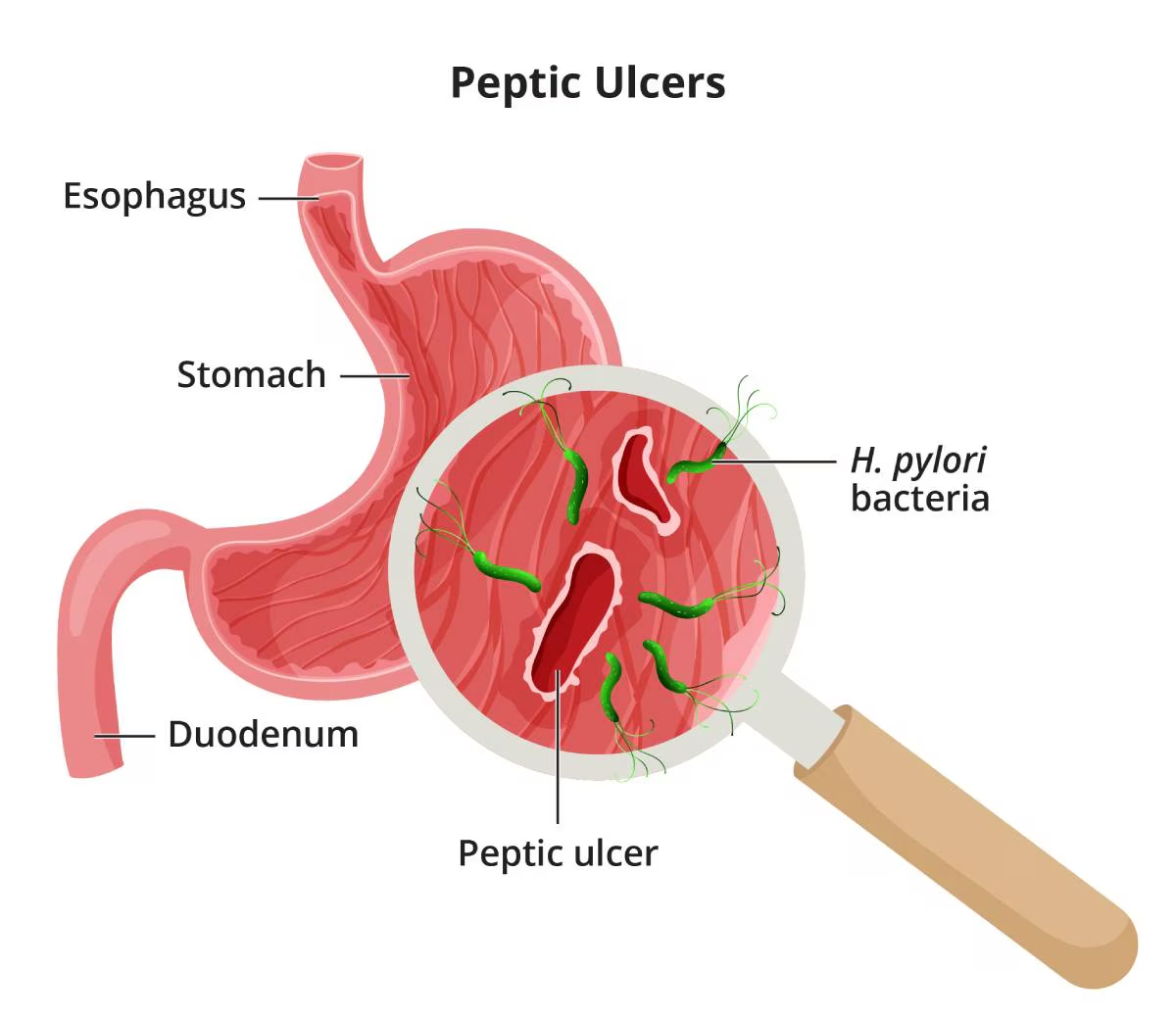
Peptic ulcers are open sores that develop on the lining of the stomach, small intestine, or esophagus. They occur when the protective mucous layer that lines these organs becomes damaged, allowing stomach acid to erode the tissue beneath. The most common types of peptic ulcers are gastric ulcers, which form in the stomach, and duodenal ulcers, which develop in the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine).
Causes of Peptic Ulcers
Understanding the causes of peptic ulcers is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. The primary culprits include:
1. Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)
H. pylori is a type of bacteria that infects the stomach lining. This infection is widespread and can lead to inflammation (gastritis) and ultimately the formation of ulcers. H. pylori is often transmitted through contaminated food or water and is a significant risk factor for developing peptic ulcers.
2. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Regular use of NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen and aspirin, can irritate the stomach lining and contribute to ulcer formation. These medications reduce inflammation and relieve pain but can compromise the protective barrier of the stomach, making it more susceptible to damage from stomach acid.
Symptoms of Peptic Ulcers
Peptic ulcers can manifest through various symptoms, which may vary in intensity and frequency. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal Pain: A burning or gnawing pain in the stomach area is the hallmark symptom of peptic ulcers. This pain often occurs when the stomach is empty and may temporarily improve after eating.
- Bloating: Many individuals with peptic ulcers experience a feeling of fullness or bloating, particularly after meals.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some people may experience nausea, and in severe cases, vomiting may occur, sometimes with blood.
- Changes in Appetite: Those with ulcers may notice a reduced appetite or unintended weight loss.
Treatment Options for Peptic Ulcers
Treating peptic ulcers typically involves a combination of medications and lifestyle changes aimed at reducing stomach acid and promoting healing.
1. Medications
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): These drugs reduce the production of stomach acid, allowing ulcers to heal. Common PPIs include omeprazole and lansoprazole.
- Antibiotics: If an H. pylori infection is present, antibiotics such as amoxicillin or clarithromycin may be prescribed to eradicate the bacteria.
- Antacids and H2-Receptor Antagonists: These medications help neutralize stomach acid and reduce symptoms.
2. Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medications, lifestyle modifications can significantly impact ulcer healing and prevent recurrence:
- Avoiding NSAIDs: If possible, limit the use of NSAIDs and opt for alternatives for pain relief.
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking can interfere with the healing of ulcers and increase their risk of recurrence.
- Limiting Alcohol: Alcohol can irritate the stomach lining, so reducing consumption can aid in healing.
Prevention Tips
Preventing peptic ulcers is possible with some proactive measures:
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands regularly and ensure that food and water sources are safe to reduce the risk of H. pylori infection.
- Be Mindful of Medications: Always consult with a healthcare professional before taking NSAIDs or other medications that may irritate the stomach lining.
- Manage Stress: While stress is not a direct cause of ulcers, it can exacerbate symptoms. Incorporating stress-reducing techniques, such as mindfulness, yoga, or exercise, can be beneficial.
Conclusion
Peptic ulcers are a common yet manageable condition. By understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms, and seeking appropriate treatment, you can effectively address peptic ulcers and reduce the risk of complications. If you suspect you have a peptic ulcer or experience persistent symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan. Remember, taking preventive measures can go a long way in maintaining your digestive health.

