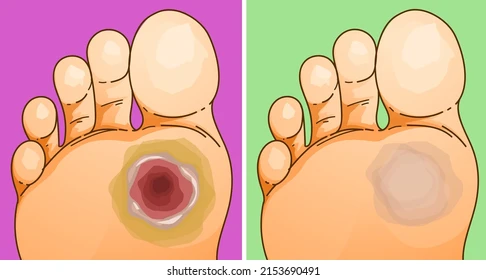
Skin ulcers are open sores that can develop on various parts of the body, often resulting from underlying health conditions or prolonged pressure. They can lead to significant discomfort and, if left untreated, can result in serious complications. Understanding the different types of skin ulcers, their causes, and how to manage and prevent them is essential for maintaining skin health. In this blog, we will explore the types of skin ulcers, their causes and risk factors, treatment options, and preventive measures.
Types of Skin Ulcers
Skin ulcers can be classified into several types based on their underlying causes and characteristics. The most common types include:
- Venous Ulcers:
- Description: These ulcers typically occur in the lower legs and ankles due to poor blood circulation. They are often associated with varicose veins and are characterized by irregularly shaped, shallow wounds with a red or yellow base.
- Symptoms: Symptoms may include swelling, pain, and discoloration in the surrounding skin.
- Arterial Ulcers:
- Description: Arterial ulcers result from inadequate blood flow to the tissues, often due to peripheral artery disease (PAD). These ulcers usually appear on the toes, feet, or lower legs and have a defined, circular shape with a pale or necrotic center.
- Symptoms: Patients may experience pain during physical activity and coldness in the affected area.
- Pressure Ulcers (Bedsores):
- Description: These ulcers develop when there is prolonged pressure on the skin, commonly affecting individuals who are bedridden or use wheelchairs. Pressure ulcers typically form over bony areas such as the heels, sacrum, and hips.
- Symptoms: Early signs include redness and skin irritation, progressing to open sores if not addressed.
Causes and Risk Factors
Skin ulcers can be attributed to various causes and risk factors, including:
- Poor Circulation: Conditions such as diabetes, peripheral artery disease, and venous insufficiency can hinder blood flow, increasing the risk of ulcers.
- Prolonged Pressure: Extended periods of immobility can lead to pressure ulcers, particularly in individuals with limited mobility.
- Infection: Bacterial infections can exacerbate existing skin conditions and lead to ulcer formation.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Insufficient intake of essential nutrients, particularly protein, vitamins C and E, and zinc, can impede skin healing and contribute to ulcer development.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Chronic illnesses such as diabetes, heart disease, and autoimmune disorders can increase susceptibility to skin ulcers.
Treatment and Management Options
Effective treatment and management of skin ulcers depend on their type and underlying cause. Common options include:
- Wound Care:
- Regular cleaning and dressing changes are crucial for all types of ulcers. Use sterile techniques to prevent infection.
- For venous ulcers, compression therapy may be recommended to improve blood flow.
- Medications:
- Topical antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent or treat infections.
- Pain relief medications can help manage discomfort.
- Surgical Interventions:
- In severe cases, surgical debridement may be necessary to remove dead tissue and promote healing.
- Vascular surgery may be considered for arterial ulcers to restore blood flow.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Maintaining a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support skin health.
- Regular exercise can improve circulation and help prevent ulcers.
Preventive Measures for Skin Health
Prevention is key to avoiding skin ulcers, particularly for individuals at higher risk. Consider the following preventive measures:
- Regular Skin Assessments:
- Routine inspections of the skin, especially in high-risk areas, can help identify early signs of ulcers.
- Pressure Relief:
- For individuals who are immobile, repositioning every two hours can reduce the risk of pressure ulcers. Using pressure-relieving devices such as specialized mattresses and cushions can also help.
- Moisturizing the Skin:
- Keeping the skin hydrated can prevent dryness and cracking, which may lead to ulcer formation.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices:
- A balanced diet, regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight contribute to overall skin health and circulation.
- Manage Chronic Conditions:
- Proper management of chronic diseases, such as diabetes and vascular conditions, is vital in reducing ulcer risk.
Conclusion
Skin ulcers can have significant implications for overall health and well-being, but understanding their types, causes, and management options is essential for effective care. By implementing preventive measures and seeking timely medical attention, individuals can reduce the risk of developing skin ulcers and promote healthier skin. If you suspect the presence of a skin ulcer, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment.

