Sexual dysfunction is often thought of primarily in physical terms, but the psychological aspects are just as significant. Mental and emotional health plays a crucial role in sexual performance and satisfaction. In this blog, we will explore the psychological components of sexual dysfunction, including common barriers, the role of therapy, and effective coping mechanisms.
Understanding Sexual Dysfunction
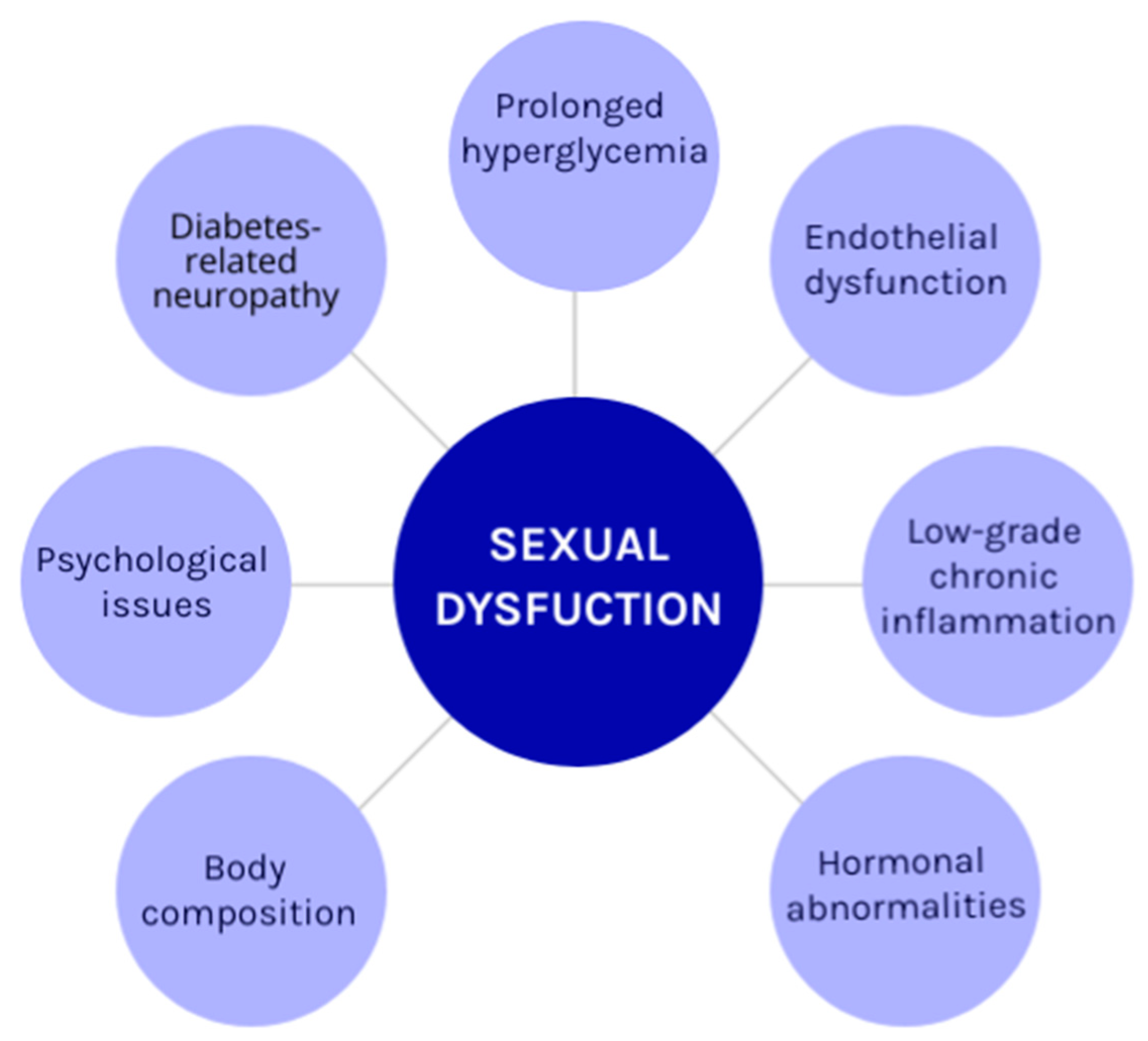
Sexual dysfunction can manifest in various ways, including low libido, erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, and difficulty achieving orgasm. While physical factors such as hormonal imbalances or medical conditions can contribute to these issues, psychological factors are often at play as well. Understanding these mental and emotional components is essential for effective treatment and resolution.
Common Psychological Barriers
- Anxiety and Stress
- Performance Anxiety: Fear of not being able to perform sexually can create a cycle of stress that exacerbates the problem.
- General Anxiety: Worries related to work, finances, or personal relationships can spill over into sexual health, reducing libido and enjoyment.
- Depression
- Depression is known to impact libido and sexual interest. Feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and fatigue can diminish the desire for intimacy and complicate sexual relationships.
- Negative Body Image
- Concerns about physical appearance can lead to decreased self-esteem, making individuals less willing to engage in sexual activities. This is particularly common in today’s society, where unrealistic body standards are prevalent.
- Past Trauma
- Experiences of sexual trauma or abuse can create psychological barriers to intimacy. Individuals may struggle with trust and emotional connection, which can hinder sexual function.
The Role of Therapy
Addressing the psychological aspects of sexual dysfunction often requires professional help. Therapy can provide a safe space for individuals and couples to explore their feelings, identify barriers, and develop coping strategies. Here are some effective therapeutic approaches:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This approach helps individuals identify negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to sexual dysfunction. CBT can empower clients to develop healthier perspectives and improve self-esteem.
- Sex Therapy: Specialized therapists can guide individuals and couples through discussions about sexual desires, boundaries, and experiences. This type of therapy often includes education about sexual health and practical techniques to enhance intimacy.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Incorporating mindfulness practices can help individuals reduce anxiety and improve focus during sexual activities. Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can promote relaxation and increase enjoyment.
Coping Mechanisms for Sexual Dysfunction
In addition to therapy, there are several self-help strategies individuals can employ to cope with the psychological aspects of sexual dysfunction:
- Open Communication
- Talking openly with partners about feelings, fears, and desires can strengthen intimacy and create a supportive environment for exploring sexual challenges. Establishing a judgment-free zone for these discussions can facilitate honesty and vulnerability.
- Focus on Intimacy, Not Performance
- Shifting the focus from performance to intimacy can reduce pressure and enhance connection. Engaging in non-sexual physical affection, such as cuddling or massage, can foster intimacy without the stress of sexual performance.
- Set Realistic Expectations
- Understanding that sexual experiences can vary and that it’s normal to face challenges can help ease anxiety. Recognizing that intimacy is about connection rather than perfection can lead to more fulfilling experiences.
- Educate Yourself
- Learning about sexual health and dysfunction can demystify the issues and provide reassurance. Resources such as books, reputable websites, and workshops can offer valuable insights into sexual health.
Conclusion
The psychological aspects of sexual dysfunction are complex and multifaceted. By understanding the emotional and mental barriers that can impact sexual health, individuals can take steps toward healing and improvement. Seeking therapy, engaging in open communication, and practicing self-compassion are essential components of overcoming sexual dysfunction.
If you or someone you know is struggling with sexual dysfunction, know that help is available. Embracing a holistic approach that addresses both physical and psychological factors can lead to a more satisfying and fulfilling sexual experience.
Call to Action
If you’re experiencing sexual dysfunction, consider reaching out to a mental health professional or a sex therapist to explore your options. Sharing your experiences in supportive communities or forums can also help alleviate feelings of isolation and provide additional insights.

