Back pain is a common issue among athletes, affecting performance and overall well-being. Understanding the causes, implementing preventative measures, and recognizing effective treatments are essential for maintaining a healthy back. In this blog, we will explore the common causes of back pain in athletes, preventative strategies, recovery tips, and the importance of core strength for back health in sports.
Common Causes of Back Pain in Athletes
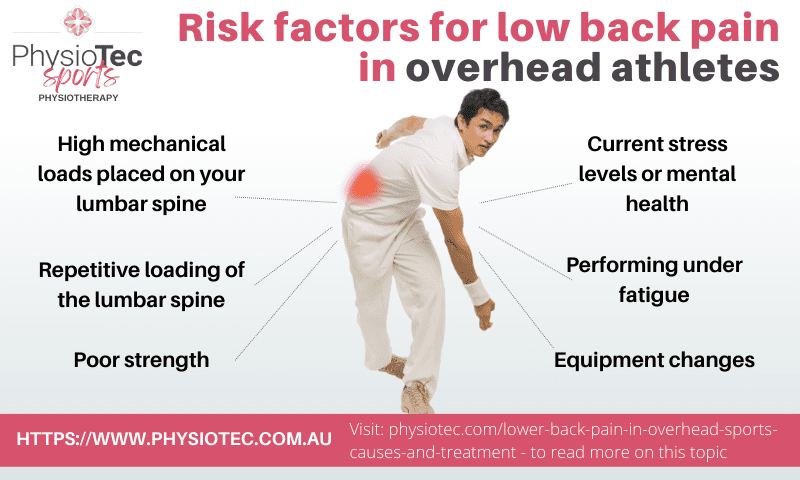
1. Overuse Injuries
Athletes often engage in repetitive movements that can lead to overuse injuries. Activities such as running, weightlifting, and swimming can place excessive strain on the back muscles and spine, resulting in discomfort and pain.
2. Acute Injuries
Acute injuries, such as sprains or strains, often occur during sports activities due to sudden movements, falls, or collisions. These injuries can cause immediate and severe pain in the back.
3. Poor Biomechanics
Improper technique during physical activities can lead to imbalances and increased stress on the back. For instance, poor running form or incorrect lifting techniques can contribute to back pain.
4. Weak Core Muscles
The core muscles play a crucial role in supporting the spine and maintaining stability during athletic movements. Weak core muscles can lead to poor posture and increased strain on the back.
5. Inadequate Warm-Up
Failing to properly warm up before exercise can increase the risk of injury. A good warm-up increases blood flow to the muscles and prepares the body for physical activity, reducing the likelihood of strain.
Preventative Measures and Recovery Tips
1. Proper Warm-Up and Cool-Down
Incorporate dynamic stretches and light cardio in your warm-up routine to prepare your muscles for activity. After workouts, engage in static stretches to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tightness.
2. Maintain Good Technique
Focus on proper biomechanics during training and competition. Working with a coach or trainer can help identify areas for improvement in your technique, reducing the risk of injury.
3. Strength Training
Incorporate strength training exercises that target the core, back, and legs. Building overall strength can enhance stability and support the spine during athletic activities.
4. Cross-Training
Engaging in different types of physical activities can help reduce the risk of overuse injuries. For example, if you’re a runner, consider incorporating swimming or cycling into your routine to provide a break for your back while maintaining fitness.
5. Listen to Your Body
Pay attention to any signs of discomfort or pain. Ignoring symptoms can lead to more severe injuries. If you experience persistent back pain, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and advice.
6. Adequate Rest and Recovery
Ensure you allow time for rest and recovery after intense training sessions. Overtraining can lead to fatigue and increase the risk of injury. Prioritize sleep and consider practices such as foam rolling or massage therapy to aid recovery.
Importance of Core Strength for Back Health in Sports
Core strength is fundamental for athletes, as it stabilizes the spine and pelvis during physical activity. A strong core helps:
- Improve Posture: Good posture reduces the strain on the back and supports optimal movement mechanics, which is essential for athletic performance.
- Enhance Performance: A strong core enables athletes to generate power and efficiency in their movements, whether running, jumping, or lifting.
- Prevent Injuries: Strengthening the core stabilizes the spine and reduces the risk of injuries, including back pain. Exercises like planks, bridges, and abdominal workouts are effective for building core strength.
Core Strengthening Exercises
- Plank: Hold a plank position for 20-60 seconds, keeping your body in a straight line from head to heels.
- Dead Bug: Lie on your back with your arms and legs raised. Lower one arm and the opposite leg towards the floor while keeping your back flat against the ground, then return to the starting position and switch sides.
- Bird Dog: Start on all fours. Extend one arm and the opposite leg simultaneously while maintaining balance. Return to the starting position and alternate sides.
Conclusion
Back pain in athletes can significantly impact performance and overall quality of life. By understanding the common causes, implementing preventative measures, and focusing on core strength, athletes can reduce their risk of injury and promote a healthy back. Prioritizing proper technique, adequate recovery, and strength training can enhance performance while keeping back pain at bay. If back pain persists, it’s crucial to seek professional guidance to address the issue and ensure a safe return to sports.

