Arthritis is a term used to describe more than 100 conditions affecting the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. While arthritis is often associated with aging, it can impact individuals of all ages and backgrounds. In this blog, we’ll explore the types of arthritis, their symptoms, and the underlying causes, helping you better understand this widespread condition.
What is Arthritis?
Arthritis is an inflammation of the joints, typically leading to pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited range of motion. It can affect one or multiple joints in the body and may develop gradually or suddenly, depending on the type.
Types of Arthritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- Overview: Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition, where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissue. This can cause joint inflammation, damage, and deformities over time.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include joint pain, swelling, redness, stiffness (especially in the morning), and fatigue. RA often affects both sides of the body symmetrically, like both wrists or both knees.
- Causes: While the exact cause of RA is unknown, factors like genetics, environmental triggers (such as smoking), and hormonal changes are thought to play a role.
- Osteoarthritis (OA)
- Overview: Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis and results from wear-and-tear of the cartilage that cushions the joints. This degeneration can lead to bone rubbing on bone, causing pain and stiffness.
- Symptoms: Symptoms include joint pain, stiffness (often after rest or inactivity), loss of flexibility, and in severe cases, joint swelling. OA typically affects the hands, knees, hips, and spine.
- Causes: The primary cause of osteoarthritis is the natural aging process, but injuries, obesity, and genetics can also increase the risk. Activities that put repetitive stress on joints can also lead to OA.
- Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA)
- Overview: Psoriatic arthritis is an inflammatory arthritis associated with psoriasis, a skin condition. People with PsA experience joint pain along with skin symptoms.
- Symptoms: Joint pain, swelling, and stiffness are common, often accompanied by psoriasis plaques on the skin. Swelling in fingers and toes, which can give a “sausage-like” appearance, is also common.
- Causes: Like RA, PsA is believed to be an autoimmune disorder. A combination of genetic, immune system, and environmental factors likely contributes to its development.
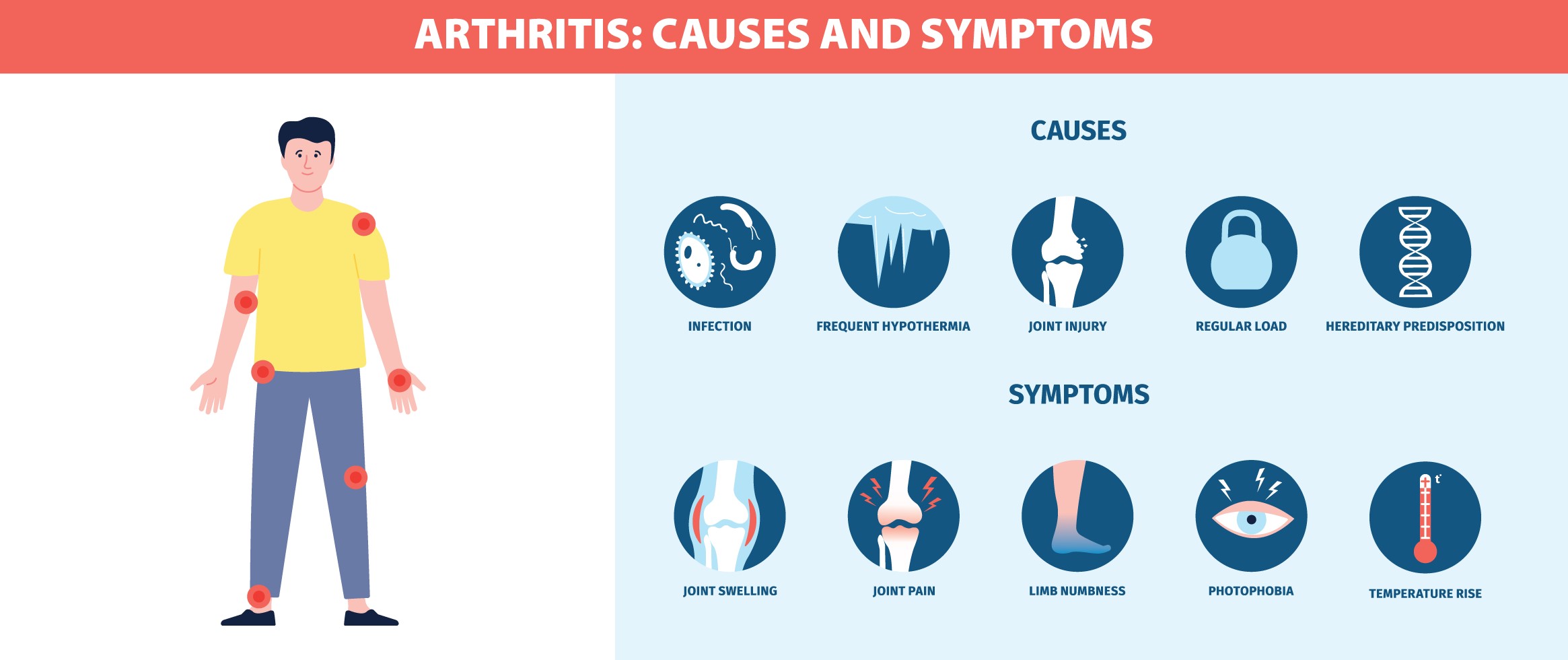
Common Symptoms of Arthritis
Understanding arthritis symptoms can help with early detection and management. Common symptoms across various types of arthritis include:
- Joint Pain: Persistent pain in affected joints.
- Stiffness: Difficulty moving joints, especially after periods of inactivity or in the morning.
- Swelling: Inflammation that can cause joints to appear larger than normal.
- Redness: Discoloration or warmth around the joint area, typically in inflammatory types of arthritis.
- Reduced Mobility: Limited range of motion in the affected joints.
- Fatigue: General feelings of tiredness and weakness, often more common in inflammatory arthritis types.
Causes of Arthritis
Arthritis can develop from a variety of factors, including:
- Genetics: A family history of arthritis may increase one’s likelihood of developing certain types, particularly autoimmune forms like RA and PsA.
- Age: Osteoarthritis risk increases with age, as joints undergo natural wear-and-tear.
- Injury: Joint injuries can lead to post-traumatic arthritis, a form of osteoarthritis that develops after physical trauma.
- Infection: Certain infections can trigger arthritis or lead to septic arthritis when the joint becomes infected.
- Immune System Dysfunction: Autoimmune conditions, such as RA and PsA, occur when the immune system attacks joint tissue.
- Lifestyle Factors: Obesity, smoking, and lack of physical activity can contribute to arthritis development and worsen symptoms.
Managing Arthritis: Prevention and Treatment Options
While there is no cure for arthritis, early diagnosis and lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms and prevent further joint damage.
- Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are commonly prescribed.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen muscles around affected joints can help improve flexibility and reduce pain.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, eating an anti-inflammatory diet, and quitting smoking can support joint health.
- Surgery: In severe cases, joint replacement or repair surgery may be recommended.
Final Thoughts
Arthritis is a complex condition that affects millions worldwide, with each type presenting its own unique set of symptoms and causes. Understanding the different types of arthritis, from rheumatoid to osteoarthritis, can empower you to make informed decisions about prevention, treatment, and lifestyle choices that support joint health. If you’re experiencing any symptoms, consulting with a healthcare professional is the first step toward effective management.

