For couples trying to conceive, it can be challenging to know when fertility issues may be at play. Infertility is generally defined as the inability to conceive after 12 months of regular, unprotected intercourse. For women over 35, it is typically recommended to seek help after six months of trying without success. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of infertility in both men and women can help couples know when it may be time to consult a fertility specialist. This blog outlines common signs of infertility in men and women, offering guidance on when to seek help.
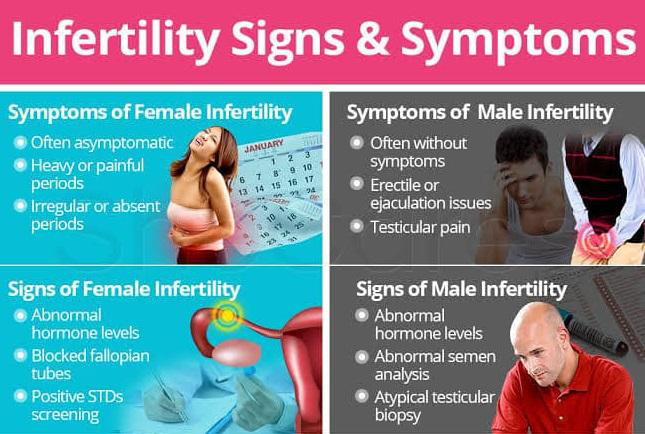
Signs of Infertility in Women
Infertility in women can stem from various factors, including hormonal imbalances, structural issues, or underlying health conditions. Here are some key symptoms that may indicate fertility issues in women:
1. Irregular Menstrual Cycles
A regular menstrual cycle is generally a positive sign of fertility. Irregular periods, including long cycles (over 35 days), very short cycles (less than 21 days), or skipped periods, can indicate hormonal imbalances that may impact ovulation.
- Causes: Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, or stress.
- Tip: Track your menstrual cycle to monitor any irregularities and discuss them with a healthcare provider if they persist.
2. Painful or Heavy Periods
Painful menstruation, or severe menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea), could be a sign of endometriosis, a condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus. Endometriosis is a common cause of infertility in women.
- Symptoms: Severe menstrual pain, pain during intercourse, or heavy bleeding.
- When to Seek Help: If period pain is intense or progressively worsening, consult a specialist.
3. Lack of Menstrual Periods (Amenorrhea)
If you have gone several months without a period (and are not pregnant), this may indicate an ovulation issue or other underlying condition.
- Causes: Amenorrhea can be due to stress, excessive exercise, PCOS, or thyroid problems.
- When to Seek Help: If your periods stop for more than three months, it’s advisable to seek medical evaluation.
4. Hormonal Changes
Symptoms such as unexplained weight gain, hair loss, acne, or excessive facial hair can signal hormonal imbalances that may impact fertility.
- Possible Causes: PCOS, thyroid issues, or elevated levels of androgens.
- When to Seek Help: If you notice multiple signs of hormonal imbalance, consider consulting a healthcare provider.
5. Pain During Intercourse
Pain during intercourse can be a sign of various conditions, including endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), or fibroids, all of which can contribute to infertility.
- Symptoms: Painful intercourse or discomfort in the pelvic region.
- When to Seek Help: Persistent pain during intercourse is a signal to discuss with a specialist.
Signs of Infertility in Men
Male infertility is often related to issues with sperm count, motility, or shape. It can be more challenging to identify without testing, but there are certain signs and symptoms to watch for:
1. Changes in Sexual Function
Issues with sexual function, including difficulties with ejaculation, reduced sexual desire, or trouble maintaining an erection, can be signs of underlying fertility problems.
- Possible Causes: Low testosterone levels, psychological factors, or chronic health conditions.
- When to Seek Help: If these issues persist, it’s beneficial to consult a doctor, as they can impact fertility.
2. Pain, Swelling, or Lumps in the Testicular Area
Pain, swelling, or a lump in the testicles could be caused by conditions like varicocele, an enlargement of veins within the scrotum that can impact sperm quality.
- When to Seek Help: Any pain, swelling, or lumps in the testicular area should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
3. Recurrent Respiratory Infections
Frequent respiratory infections may indicate cystic fibrosis, which can affect male fertility. This genetic condition often impacts the vas deferens, the tube that carries sperm from the testicles.
- When to Seek Help: If you experience recurring respiratory issues and are struggling with fertility, genetic testing may be recommended.
4. Small or Firm Testicles
The size and texture of the testicles can indicate issues with sperm production. Smaller or firmer testicles may be a sign of conditions affecting sperm count and quality.
- When to Seek Help: If you have concerns about testicular health, a doctor can provide an examination and conduct further tests if necessary.
5. Low Sperm Count or Poor Sperm Quality
Low sperm count, poor motility (movement), or abnormal sperm shape can hinder fertility. Often, men are unaware of sperm-related issues until they undergo a semen analysis.
- When to Seek Help: If you have been trying to conceive for over a year without success, a semen analysis can provide insight into potential fertility issues.
When to Seek Help: General Guidelines
For both men and women, knowing when to seek help can be challenging. Here are general guidelines for consulting a fertility specialist:
- If you are under 35 and have been trying to conceive for over 12 months without success, it’s advisable to seek medical evaluation.
- If you are over 35, seek help after six months of trying without success.
- If you are over 40, consulting a specialist sooner can help, as fertility naturally declines with age.
Additionally, if you experience any of the signs or symptoms discussed, it may be beneficial to consult a healthcare provider sooner rather than later.
Final Thoughts
Recognizing the signs of infertility early on can help couples take proactive steps toward understanding and addressing potential fertility issues. By identifying symptoms like irregular periods, painful intercourse, changes in sexual function, or testicular pain, couples can seek the appropriate medical guidance and explore treatment options. Consulting a fertility specialist is a positive step for many, as it offers a clearer picture of one’s reproductive health and opens the door to potential solutions.

