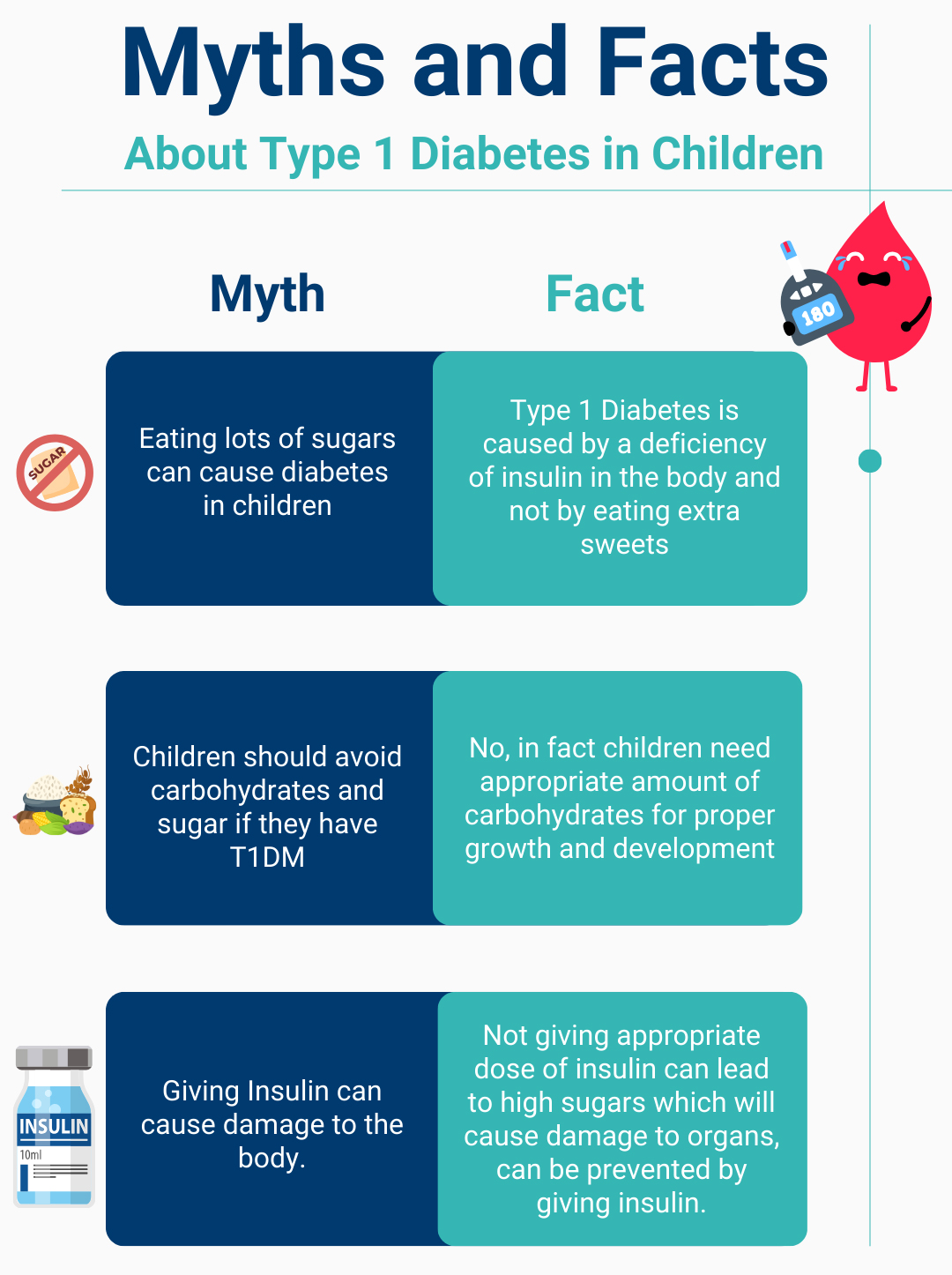
Diabetes is one of the most prevalent chronic conditions globally, yet there are still many misconceptions surrounding it. Misinformation can lead to unnecessary worry, mismanagement, and even stigmatization. Let’s dive into some of the most common myths about diabetes and debunk them with the facts.
Myth 1: Eating Too Much Sugar Causes Diabetes
Fact: While diet does play a role in managing diabetes, eating sugar alone does not directly cause diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition, while Type 2 diabetes is influenced by a combination of genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Consuming excess calories, regardless of the source, can lead to obesity, which is a risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. However, diabetes is more complex than simply eating too much sugar.
Myth 2: Only Overweight People Get Diabetes
Fact: Obesity is a risk factor, especially for Type 2 diabetes, but many people with diabetes are not overweight. Type 1 diabetes, an autoimmune condition, can affect people of all shapes and sizes. Even for Type 2 diabetes, factors like age, family history, and ethnic background can play a significant role, regardless of weight.
Myth 3: Diabetics Can’t Eat Carbs or Sugar at All
Fact: Carbohydrates and sugar can still be a part of a balanced diet for people with diabetes, but portion control and careful meal planning are essential. Carbohydrates affect blood sugar, so people with diabetes must monitor their intake and focus on low-glycemic, high-fiber options. With proper planning, even an occasional treat can be enjoyed in moderation.
Myth 4: Diabetes Isn’t a Serious Condition
Fact: Diabetes can lead to serious health complications if not properly managed. Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can cause nerve damage, heart disease, kidney failure, and vision problems. With consistent management, a healthy diet, and regular check-ups, people with diabetes can lead a full, healthy life, but it’s important not to underestimate the condition.
Myth 5: Insulin is Only Needed for Severe Diabetes
Fact: Many people believe insulin is only for those with “severe” diabetes, but this isn’t true. People with Type 1 diabetes require insulin for survival. In Type 2 diabetes, insulin may be introduced if blood sugar levels are not manageable through diet, exercise, and oral medications alone. The need for insulin doesn’t necessarily mean the diabetes is “severe,” but rather that blood sugar control requires additional support.
Myth 6: People with Diabetes Can’t Exercise
Fact: Exercise is one of the best tools for managing diabetes. Physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity, aiding blood sugar control. Regular exercise can also reduce the risk of complications. However, people with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels and consult with a healthcare provider to ensure safe exercise routines.
Myth 7: If You Don’t Have Symptoms, You Don’t Have Diabetes
Fact: Many people with Type 2 diabetes experience few or no symptoms, especially in the early stages. Often, diabetes is only detected during routine blood tests. This is why regular screening is crucial, especially for those with risk factors such as family history, obesity, or sedentary lifestyle.
Myth 8: Taking Insulin Means You’ve Failed to Manage Your Diabetes
Fact: Insulin is a natural part of diabetes treatment for many, especially those with Type 1 diabetes. For people with Type 2 diabetes, it may become necessary over time due to the progressive nature of the disease. Needing insulin doesn’t mean failure; it’s simply another way to keep blood sugar levels under control and prevent complications.
Myth 9: You Can “Cure” Diabetes with Diet and Exercise
Fact: Type 1 diabetes is not curable, and while lifestyle changes can greatly impact Type 2 diabetes management, they don’t eliminate it entirely. Diet and exercise can help manage blood sugar levels, and some individuals may achieve remission, but diabetes is typically a lifelong condition. Management is essential, even if blood sugar levels are within a healthy range.
Myth 10: Diabetes Only Affects Blood Sugar
Fact: Diabetes can affect almost every part of the body. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, nerves, and organs, leading to complications such as neuropathy, vision problems, kidney disease, and cardiovascular issues. Good diabetes management and regular check-ups are vital to monitoring and minimizing these risks.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the truth about diabetes can empower individuals to manage their condition more effectively and reduce stigma around it. Diabetes is complex, and misconceptions can prevent people from getting the help they need. By separating fact from fiction, we can all work towards a more informed and supportive community for people living with diabetes.

