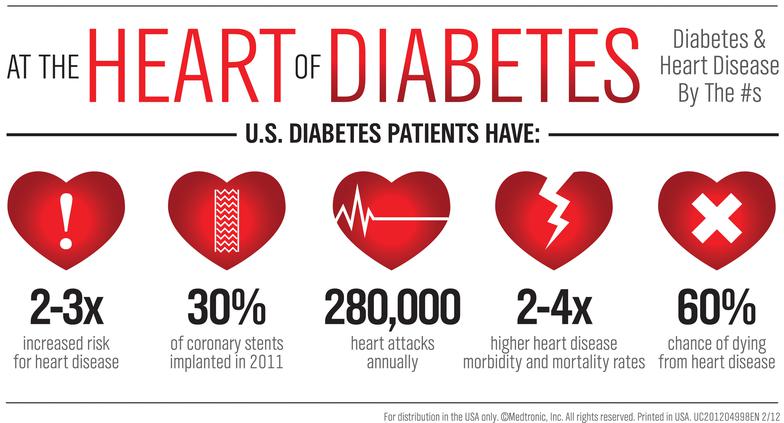
People with diabetes are at an increased risk of developing heart disease, a leading cause of complications and mortality in those with diabetes. Managing blood sugar alone isn’t enough; understanding and reducing cardiovascular risk factors is crucial for overall health. This blog explores the link between diabetes and heart disease and provides practical tips to protect your heart.
The Link Between Diabetes and Heart Disease
High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, increasing the likelihood of cardiovascular complications. Diabetes also raises the risk of other heart disease contributors, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and obesity. Over time, these risk factors can lead to atherosclerosis (plaque buildup in arteries), increasing the chance of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular issues.
1. Control Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining stable blood sugar is essential for preventing damage to blood vessels and nerves. Work with your healthcare provider to monitor blood sugar regularly and keep it within the target range. Consider using a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) or regular testing to track fluctuations.
Tips:
- Follow a balanced diet that limits refined sugars and carbohydrates.
- Incorporate more fiber-rich foods like vegetables, legumes, and whole grains.
- Take medications as prescribed and avoid skipping doses.
2. Manage Blood Pressure
High blood pressure (hypertension) often accompanies diabetes, further increasing cardiovascular risks. Over time, high blood pressure can lead to artery damage, heart attack, and stroke. A target blood pressure of below 140/90 mm Hg is generally recommended for people with diabetes, though this can vary by individual.
Tips:
- Reduce sodium intake by limiting processed foods and choosing fresh ingredients.
- Stay hydrated and avoid excessive caffeine or alcohol.
- Include potassium-rich foods like bananas, spinach, and avocados.
3. Monitor and Control Cholesterol Levels
People with diabetes often have higher levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol, which can contribute to plaque buildup in arteries. Monitoring cholesterol levels can help reduce cardiovascular risk.
Tips:
- Aim to consume healthy fats from sources like olive oil, nuts, and fish.
- Avoid trans fats commonly found in processed and fried foods.
- Regular exercise can help increase HDL (good) cholesterol while lowering LDL.
4. Prioritize Physical Activity
Regular exercise is beneficial for blood sugar control, weight management, and heart health. Physical activity improves blood flow, strengthens the heart, and enhances insulin sensitivity.
Tips:
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
- Include strength training twice a week to build muscle and improve glucose metabolism.
- If you’re new to exercise, start slow and gradually increase your intensity and duration.
5. Quit Smoking
Smoking significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, especially in those with diabetes. Smoking damages blood vessels, raises blood pressure, and can lead to unhealthy cholesterol levels.
Tips:
- Seek support through counseling, nicotine replacement therapy, or support groups.
- Replace smoking with healthier habits, like walking, drinking water, or chewing sugar-free gum.
- Remember that quitting smoking has almost immediate benefits for heart health.
6. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, is linked to insulin resistance and increased cardiovascular risk. Losing even a small percentage of body weight can improve blood pressure, blood sugar, and cholesterol levels.
Tips:
- Focus on a balanced diet rich in lean proteins, whole grains, and vegetables.
- Practice portion control and mindful eating.
- Avoid skipping meals, which can lead to overeating later in the day.
7. Reduce Stress Levels
Chronic stress contributes to high blood pressure and unhealthy eating habits, increasing heart disease risk. Managing stress effectively can support both heart and blood sugar health.
Tips:
- Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
- Take short breaks during the day to stretch or go for a quick walk.
- Make time for hobbies and activities that bring you joy and relaxation.
8. Stay on Top of Medical Check-Ups
Regular check-ups can help catch any potential heart issues early and ensure that your diabetes is managed effectively. These appointments allow your doctor to monitor key markers, including A1C levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol.
Tips:
- Schedule annual check-ups and lab work to monitor health markers.
- Regularly communicate with your healthcare team about any symptoms or concerns.
- Stay up-to-date on recommended screenings and preventive tests.
Final Thoughts
The connection between diabetes and heart health is clear, but with proactive measures, you can reduce your risk of cardiovascular complications. Small, sustainable lifestyle changes—like adopting a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress—can make a significant impact on your overall health. Remember, managing diabetes effectively also means taking care of your heart.

