Insulin resistance is a critical metabolic condition that can significantly impact your overall health and is closely linked to the development of type 2 diabetes. Understanding insulin resistance, its causes, symptoms, and preventive measures is essential for managing your health effectively. In this blog, we’ll explore these aspects in detail and offer practical tips to help you manage or prevent insulin resistance.
What is Insulin Resistance?
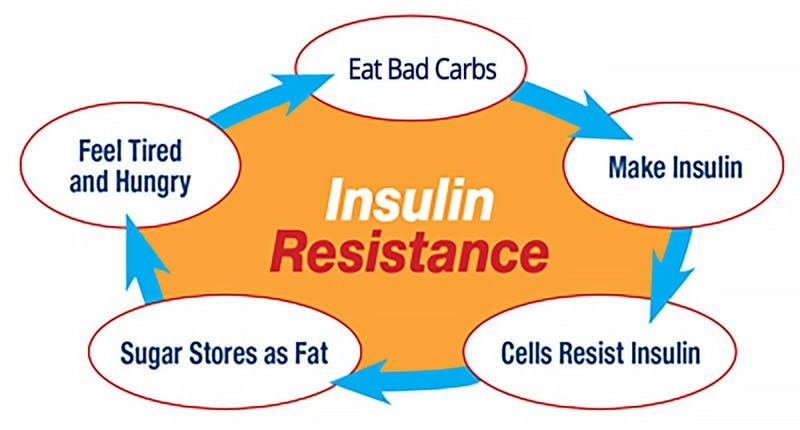
Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels. In a healthy individual, insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into the cells for energy. When cells become resistant to insulin, the pancreas compensates by producing more insulin, which can eventually lead to elevated blood sugar levels and, if left unmanaged, type 2 diabetes.
Causes of Insulin Resistance
Understanding the underlying causes of insulin resistance can help you take preventive measures. Some of the main factors include:
- Obesity: Excess body fat, particularly around the abdomen, is one of the primary contributors to insulin resistance. Fat cells release inflammatory substances that interfere with insulin signaling.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can contribute to weight gain and decreased insulin sensitivity. Regular exercise is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight and improving insulin sensitivity.
- Diet: A diet high in refined carbohydrates, added sugars, and unhealthy fats can contribute to insulin resistance. Overeating and frequent consumption of processed foods can lead to weight gain and metabolic dysfunction.
- Genetics: Family history and genetics can play a role in developing insulin resistance. If you have a family history of type 2 diabetes, you may be at higher risk.
- Hormonal Changes: Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can lead to hormonal imbalances that contribute to insulin resistance.
- Chronic Stress: High stress levels can elevate cortisol, a hormone that can contribute to insulin resistance. Managing stress is crucial for overall health.
Symptoms of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance can develop gradually, and many people may not experience noticeable symptoms initially. However, some common signs include:
- Increased Hunger: Persistent feelings of hunger, even after eating, can indicate that your body isn’t effectively utilizing glucose for energy.
- Fatigue: Low energy levels or fatigue can result from the body’s inability to use insulin effectively.
- Weight Gain: Particularly around the abdomen, weight gain can be a significant indicator of insulin resistance.
- Dark Patches on Skin: Acanthosis nigricans, a condition characterized by dark, velvety patches of skin, often appears in areas like the neck, armpits, or groin.
- High Blood Sugar Levels: Elevated blood sugar levels, often identified through regular screenings, can indicate insulin resistance.
Prevention and Management Tips
While insulin resistance can be concerning, there are several lifestyle changes you can adopt to prevent or manage the condition:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Aim to achieve and maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise. Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% can improve insulin sensitivity.
- Adopt a Balanced Diet:
- Focus on whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit processed foods, refined carbohydrates, and sugary beverages.
- Incorporate fiber-rich foods, which can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
- Engage in Regular Physical Activity:
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Incorporate strength training exercises at least twice a week.
- Physical activity helps increase insulin sensitivity and aids in weight management.
- Manage Stress:
- Practice stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing, or mindfulness. Regular relaxation can help regulate hormone levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Get Enough Sleep:
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Poor sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate appetite and insulin sensitivity.
- Monitor Your Health:
- Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help monitor blood sugar levels and other risk factors. If you’re at risk for diabetes, discuss a screening schedule with your doctor.
Conclusion
Understanding insulin resistance is crucial for preventing or managing diabetes. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and effective stress management, you can significantly improve your insulin sensitivity and overall health. If you suspect you may be insulin resistant or are experiencing symptoms, consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and support.

