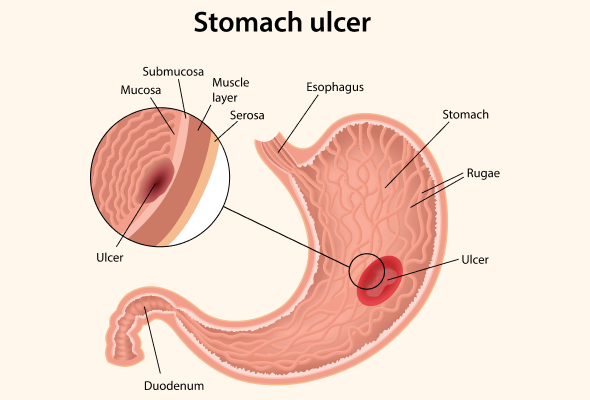
Peptic ulcers are painful sores that can develop in the lining of the stomach or the first part of the small intestine. They can be caused by various factors, including Helicobacter pylori infection, the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and excess stomach acid. Effective treatment typically involves a combination of medications aimed at reducing symptoms, promoting healing, and preventing complications. This comprehensive guide will explore common medications used for ulcer treatment, how they work, potential side effects and interactions, and the importance of following prescribed treatment.
Common Medications
1. Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
Proton pump inhibitors are among the most commonly prescribed medications for ulcer treatment. They work by blocking the proton pump in the stomach lining, which significantly reduces the production of stomach acid.
- Examples: Omeprazole (Prilosec), Esomeprazole (Nexium), Lansoprazole (Prevacid).
- Indications: Used to treat peptic ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
2. H2 Receptor Antagonists (H2 Blockers)
H2 blockers also reduce stomach acid, but they work differently from PPIs. They inhibit histamine action on the H2 receptors in the stomach lining, leading to decreased acid secretion.
- Examples: Ranitidine (Zantac), Famotidine (Pepcid), Nizatidine (Axid).
- Indications: Effective for treating ulcers, GERD, and conditions that cause excess stomach acid.
3. Antacids
Antacids are over-the-counter medications that neutralize stomach acid, providing quick relief from ulcer-related discomfort. They do not promote healing but can alleviate symptoms.
- Examples: Calcium carbonate (Tums), Magnesium hydroxide (Milk of Magnesia), Aluminum hydroxide.
- Indications: Used for symptomatic relief of heartburn, indigestion, and upset stomach.
4. Antibiotics
If an ulcer is caused by H. pylori infection, antibiotics are often prescribed as part of a combination therapy to eradicate the bacteria and promote healing.
- Examples: Amoxicillin, Clarithromycin, Metronidazole.
- Indications: Typically used in conjunction with PPIs or H2 blockers in a treatment regimen known as triple therapy.
How They Work to Reduce Symptoms
- PPIs: By inhibiting the proton pump, PPIs effectively decrease gastric acid production, allowing the ulcer to heal while also reducing symptoms such as pain and discomfort associated with acid exposure.
- H2 Blockers: These medications reduce the amount of acid secreted by the stomach, leading to decreased irritation of the ulcer and relief from symptoms.
- Antacids: They provide immediate relief by neutralizing stomach acid and alleviating symptoms of heartburn and discomfort but do not address the underlying cause of ulcers.
- Antibiotics: When used to treat H. pylori infections, antibiotics help eliminate the bacteria, which can significantly aid in ulcer healing and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions
While medications for ulcer treatment are generally safe and effective, they can cause side effects and interact with other medications. It’s essential to be aware of these potential issues:
1. PPIs
- Common Side Effects: Nausea, diarrhea, constipation, headache, dizziness.
- Serious Side Effects: Long-term use may lead to vitamin B12 deficiency, kidney disease, or increased risk of gastrointestinal infections.
- Drug Interactions: May interact with certain medications, including blood thinners and antifungal drugs, potentially affecting their efficacy.
2. H2 Blockers
- Common Side Effects: Drowsiness, dizziness, constipation, diarrhea.
- Serious Side Effects: Rarely, they may cause confusion or liver issues, especially in older adults or those with liver problems.
- Drug Interactions: Can affect the absorption of other medications taken simultaneously.
3. Antacids
- Common Side Effects: Constipation or diarrhea, depending on the active ingredient.
- Serious Side Effects: Prolonged use can lead to electrolyte imbalances and kidney problems.
- Drug Interactions: Can interfere with the absorption of other medications; it’s generally advised to take them at least two hours apart from other drugs.
4. Antibiotics
- Common Side Effects: Nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain.
- Serious Side Effects: Risk of allergic reactions, Clostridium difficile infection, and antibiotic resistance.
- Drug Interactions: May interact with anticoagulants, other antibiotics, and medications that affect liver enzymes.
Importance of Following Prescribed Treatment
Adhering to the prescribed treatment plan for ulcers is crucial for several reasons:
- Promotes Healing: Consistent use of medications like PPIs and antibiotics helps ensure that the ulcer heals properly, reducing the risk of complications such as bleeding or perforation.
- Prevents Recurrence: Following the treatment plan can reduce the chances of future ulcer development, especially if the underlying cause (such as H. pylori infection) is addressed.
- Manages Symptoms: Taking medications as directed helps control symptoms, improving the quality of life for individuals suffering from ulcer-related discomfort.
- Avoids Complications: Inadequate treatment or premature discontinuation of medications can lead to complications that may require more intensive medical interventions.
- Consultation with Healthcare Provider: Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider allow for monitoring of progress, adjustments to treatment as necessary, and assessment of any side effects or interactions.
Conclusion
Medications play a vital role in the effective treatment of peptic ulcers, helping to alleviate symptoms, promote healing, and prevent complications. Common medications include proton pump inhibitors, H2 blockers, antacids, and antibiotics. Understanding how these medications work, their potential side effects and interactions, and the importance of adhering to prescribed treatment can empower individuals to take control of their ulcer management. If you have concerns about your ulcer treatment or experience any adverse effects, consult your healthcare provider for guidance and support. By following a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals can pave the way toward healing and a return to a healthier lifestyle.

