Back pain is a common ailment that can significantly impact daily life. Understanding the differences between chronic and acute back pain is essential for effective treatment and management. This blog will explore the definitions, causes, treatment options, and guidance on when to seek medical advice for both types of back pain.
Differences Between Acute and Chronic Pain
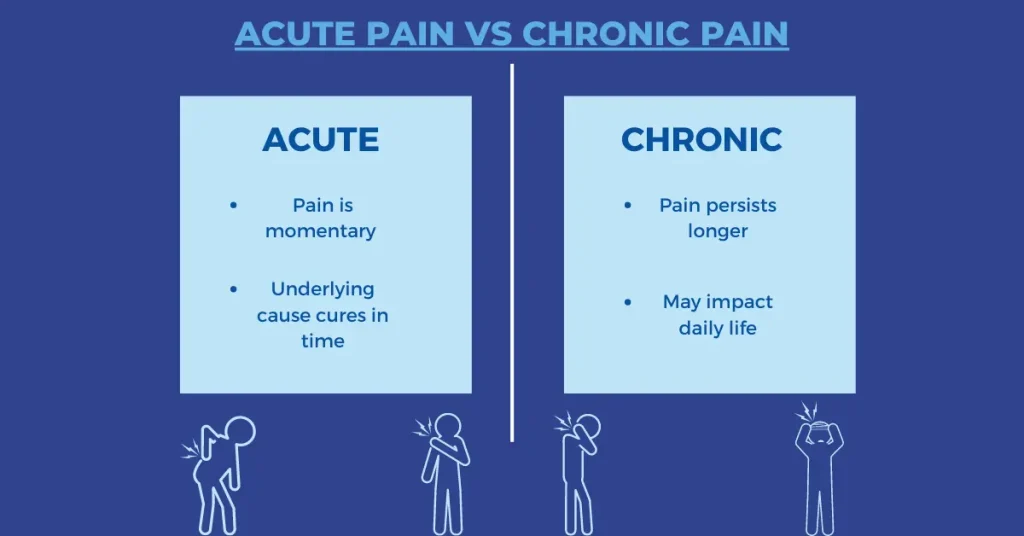
Acute Back Pain:
- Definition: Acute back pain is defined as pain that lasts for a short period, usually less than six weeks. It often arises suddenly, often following an injury, strain, or specific event.
- Characteristics: The pain is typically sharp or intense and may be accompanied by muscle spasms. Acute pain usually resolves with rest, treatment, and time.
- Duration: Most people experience acute back pain as a temporary condition that improves with appropriate care.
Chronic Back Pain:
- Definition: Chronic back pain is characterized by pain that persists for three months or longer, even after the initial injury or cause has been treated or resolved.
- Characteristics: The pain can be continuous or intermittent, ranging from mild to severe. Chronic pain often involves a more complex interplay of physical, psychological, and environmental factors.
- Duration: Chronic pain may not always correlate with the severity of the underlying condition, and it can last for years, affecting quality of life and daily activities.
Common Causes and Treatment Options
Causes of Acute Back Pain:
- Injury or Strain: Lifting heavy objects, sudden movements, or awkward twisting can cause muscle strains or ligament sprains.
- Herniated Discs: Discs can bulge or rupture, pressing on nearby nerves and causing pain.
- Skeletal Irregularities: Conditions such as scoliosis can lead to acute pain when the spine is strained.
Treatment Options for Acute Back Pain:
- Rest and Ice/Heat Therapy: Resting the affected area and applying ice or heat can reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen can help manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen back muscles and improve flexibility.
- Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that aggravate the pain while gradually reintroducing normal activities can promote healing.
Causes of Chronic Back Pain:
- Degenerative Disc Disease: Discs can wear down over time, leading to pain as the vertebrae compress nerves.
- Arthritis: Conditions like osteoarthritis can cause inflammation and pain in the spine and surrounding joints.
- Fibromyalgia: This chronic pain condition can lead to widespread pain, including the back.
- Previous Injuries: Untreated or improperly treated acute injuries can lead to chronic pain conditions.
Treatment Options for Chronic Back Pain:
- Long-Term Physical Therapy: Ongoing physical therapy can help manage pain and improve function.
- Medications: Prescription medications, including muscle relaxants, opioids, or anticonvulsants, may be necessary for managing chronic pain.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture, chiropractic care, and massage therapy can provide relief for chronic pain sufferers.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Weight management, regular exercise, and ergonomic adjustments in the workplace can help reduce chronic pain episodes.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Seek Medical Attention for Acute Back Pain if:
- Severe Pain: If the pain is intense and does not improve with rest or over-the-counter medications.
- Nerve Symptoms: Experiencing numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs or feet.
- Loss of Bladder or Bowel Control: This could indicate a serious condition requiring immediate attention.
- Persistent Pain: If pain lasts longer than a few weeks despite treatment.
Seek Medical Attention for Chronic Back Pain if:
- Impact on Daily Life: If the pain interferes with your ability to perform daily activities or work.
- Progressive Symptoms: If the pain is worsening over time or becoming more frequent.
- Previous Treatments Have Failed: If prior treatments, including physical therapy or medications, have not provided relief.
- Accompanying Symptoms: If chronic back pain is accompanied by unexplained weight loss, fever, or significant changes in health.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between acute and chronic back pain is crucial for effective management and treatment. While acute back pain often resolves with appropriate care, chronic back pain can require ongoing attention and a comprehensive approach to treatment. If you’re experiencing persistent or severe back pain, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized care plan. Don’t let back pain hold you back—take proactive steps to seek relief and improve your quality of life!

