When you measure your blood pressure, you’re given two numbers, such as “120/80.” But what exactly do these numbers mean, and how do they relate to your overall health? Understanding blood pressure readings is essential for recognizing hypertension and taking proactive steps to protect your heart.
In this article, we’ll break down blood pressure readings, explain the significance of each number, and offer tips on how to monitor your blood pressure effectively.
The Basics of Blood Pressure Readings
Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is recorded with two numbers: systolic and diastolic.
- Systolic Pressure: This is the top number in a blood pressure reading. It measures the force your heart exerts on the walls of your arteries with each heartbeat.
- Diastolic Pressure: This is the bottom number. It indicates the force exerted by the blood on the artery walls when your heart is at rest between beats.
For example, in a reading of 120/80 mmHg, “120” is the systolic pressure, and “80” is the diastolic pressure.
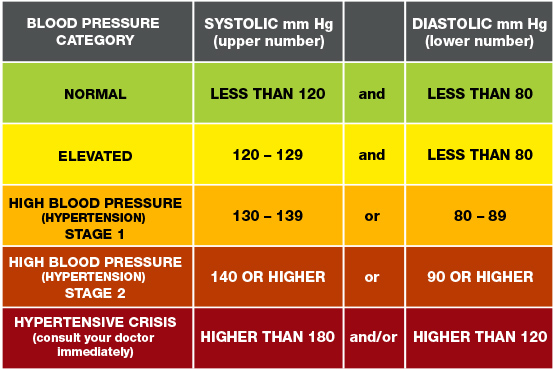
What Do Blood Pressure Numbers Mean?
Blood pressure readings fall into different categories that help identify healthy ranges as well as stages of hypertension. Here’s a breakdown:
1. Normal Blood Pressure
- Reading: Less than 120/80 mmHg
- Meaning: This range is considered ideal for healthy blood flow and heart health. People in this range should aim to maintain their blood pressure through a balanced lifestyle.
2. Elevated Blood Pressure
- Reading: Systolic between 120-129 and diastolic less than 80 mmHg
- Meaning: Elevated blood pressure isn’t yet hypertension, but it indicates that you’re at risk. Lifestyle changes like diet improvement, regular exercise, and stress management can help prevent progression to hypertension.
3. Hypertension Stage 1
- Reading: Systolic between 130-139 or diastolic between 80-89 mmHg
- Meaning: At this stage, your risk of heart disease and stroke increases. Your doctor may recommend lifestyle changes, and in some cases, medication may be prescribed to lower your blood pressure.
4. Hypertension Stage 2
- Reading: Systolic 140 or higher or diastolic 90 mmHg or higher
- Meaning: This level indicates more severe hypertension, often requiring a combination of lifestyle adjustments and medication to bring blood pressure down to a healthier range.
5. Hypertensive Crisis
- Reading: Systolic over 180 and/or diastolic over 120 mmHg
- Meaning: This is a dangerous, life-threatening situation that requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms may include severe headache, shortness of breath, chest pain, and vision problems. If you receive this reading, seek emergency care immediately.
Why Are Both Systolic and Diastolic Numbers Important?
Both the systolic and diastolic numbers provide insights into heart health and risk levels.
- Systolic Pressure: This number often receives more attention because high systolic pressure is strongly linked to cardiovascular disease, particularly in older adults. It indicates the force needed to pump blood from the heart, and elevated systolic pressure can signal stiffened arteries.
- Diastolic Pressure: Diastolic pressure is especially important for younger individuals. Elevated diastolic pressure over time can contribute to arterial damage and heart disease.
Together, these numbers provide a complete picture of blood flow and heart function, helping doctors identify and manage hypertension effectively.
Why Accurate Blood Pressure Readings Matter
Regular and accurate blood pressure readings are essential for tracking your health. Here’s why:
- Early Detection of Hypertension: Regular readings can reveal high blood pressure early on, allowing you to take preventive action.
- Tracking Treatment Effectiveness: If you’re already managing hypertension, regular readings show how well your treatment is working.
- Preventing Complications: Consistent high blood pressure can lead to heart disease, kidney problems, and vision issues. Monitoring helps catch changes early.
Tips for Accurate Blood Pressure Measurement
To get an accurate reading, keep these tips in mind:
- Use a Reliable Device: Consider a digital blood pressure monitor for home use, and ensure it’s validated and regularly calibrated.
- Measure at the Same Time Daily: Blood pressure can fluctuate, so measure it at a consistent time each day, ideally in the morning.
- Rest Before Measurement: Sit quietly for 5 minutes before taking a reading to avoid elevated numbers due to physical activity or stress.
- Sit Properly: Sit with your back supported, feet flat on the floor, and arm at heart level. Avoid talking during the measurement.
- Take Multiple Readings: Take two or three readings at one sitting, a minute apart, and calculate the average for accuracy.
- Avoid Certain Triggers: Caffeine, exercise, and smoking can temporarily raise blood pressure, so avoid these before taking a measurement.
Managing Blood Pressure for Long-Term Health
Understanding your blood pressure readings is the first step to better heart health. Here are additional ways to keep your blood pressure in check:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Emphasize whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy. Limiting salt, saturated fats, and sugar can also help.
- Exercise Regularly: Aim for 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week, such as brisk walking or cycling.
- Limit Alcohol and Quit Smoking: Both habits contribute to higher blood pressure and cardiovascular risks.
- Manage Stress: Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress-related blood pressure spikes.
Conclusion
Blood pressure readings may seem like a series of numbers, but they provide critical insights into your heart health and overall wellness. By understanding what systolic and diastolic pressures indicate and tracking your numbers regularly, you can take control of your health, reduce the risk of complications, and enjoy a healthier life. Make regular blood pressure checks part of your routine, and don’t hesitate to seek medical advice if your readings indicate a potential problem.
With the right information and lifestyle choices, managing blood pressure is achievable, helping you protect your heart and ensure long-term well-being.

